UrgoClean safely and effectively removes slough and debris from the wound, to ensure the wound bed is prepared for healing.
PROPERTIES
- Traps slough effectively and manages minor bleeding (1,2)
- Absorbs exudate while preventing the wound from becoming macerated (3), protecting the peri-wound skin
- Keeps the bottom of the wound clean (maintenance debridement)(2,4)
- Assures atraumatic and painless removal for the patient (2,5)
INDICATIONS
UrgoClean is indicated for the treatment of exuding wounds in the desloughing phase (chronic wounds and acute wounds).
UrgoClean Rope is used for the treatment of cavity wounds.
Contraindications
• Known sensitivity to the dressing or its components
• Do not use UrgoClean as a surgical sponge for heavily bleeding wounds.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
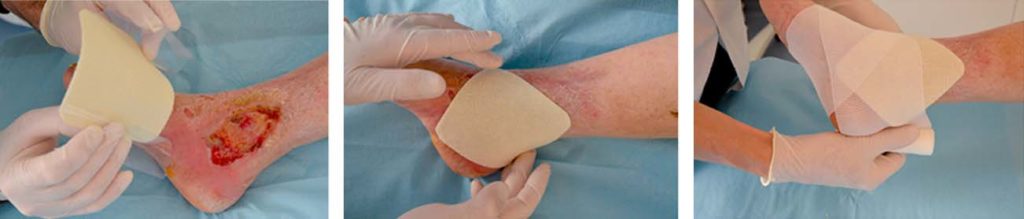
- Clean the wound according to local protocol, then rinse with normal saline. If an antiseptic has previously been used, rinse the wound carefully with normal saline before applying UrgoClean
- The use of UrgoClean does not dispense with the need for mechanical debridement where required.
- Remove the protective tabs
- UrgoClean can be cut using sterile scissors to adjust the size of the dressing to the wound if necessary
- Apply the soft-adherent side of UrgoClean to the wound and its contours
- Cover UrgoClean with a secondary dressing suitable for the location of the wound and level of exudate.
UrgoClean has the ability to be left in place for up to 7 days, however during the early desloughing phase it may warrant more frequent dressing changes but this should be based on the clinical assessment. Discard any unused parts of the dressing according to local procedures.
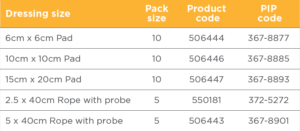
FORMATS
CLINICAL EVIDENCE
- Data on file Urgo, report n°88050-2009.
- Meaume S. et al., Evaluation of two fibrous wound dressings for the management of leg ulcers: Results of a European randomised controlled trial (EARTH RCT). J Wound Care, Vol 23, No 3; March 2014, 105-116.
- Meaume S. et al., Management of chronic wounds with an innovative absorbent wound dressing. J Wound Care, Vol 21, No 7; July 2012, 315-322.
- Percival SL, et al. Slough and biofilm: removal of barriers to wound healing by desloughing. J Wound Care. 2015 Nov; 24(11):498,500-3,506-10.
- Meaume et al., The importance of pain reduction through dressing selection in routine wound management: the MAPP study, Journal of Wound Care, 2004, Vol 13, No 10, 409-413.